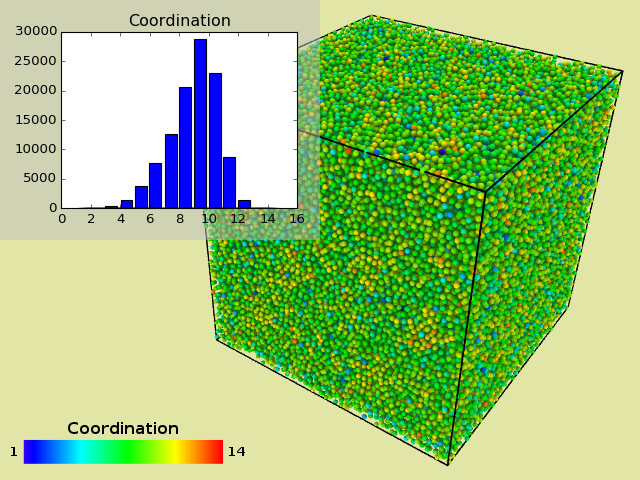
Example O2: Including data plots in rendered images¶
This user-defined viewport overlay function demonstrates how to use the Matplotlib Python module to render the radial
distribution function, which is dynamically computed by a CoordinationAnalysisModifier
in the data pipeline, on top the three-dimensional visualization.
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg') # Activate 'agg' backend for off-screen plotting.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import PySide2.QtGui
def render(args):
# Request the results of the pipeline at the animation time currently being rendered:
data = args.scene.selected_pipeline.compute(args.frame)
# Look up the DataTable generated by the CoordinationAnalysisModifier:
if 'coordination-rdf' not in data.tables:
raise RuntimeError('No RDF data found')
rdf_data = data.tables['coordination-rdf'].xy()
# Compute plot size in inches (DPI determines label size)
dpi = 80
plot_width = 0.5 * args.size[0] / dpi
plot_height = 0.5 * args.size[1] / dpi
# Create matplotlib figure:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(plot_width,plot_height), dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0.5)
plt.title('Coordination')
# Plot RDF histogram data
ax.bar(rdf_data[:,0], rdf_data[:,1])
plt.tight_layout()
# Render figure to an in-memory buffer.
buf = fig.canvas.print_to_buffer()
plt.close(fig)
# Create a QImage from the memory buffer
res_x, res_y = buf[1]
img = PySide2.QtGui.QImage(buf[0], res_x, res_y, PySide2.QtGui.QImage.Format_RGBA8888)
# Paint QImage onto viewport canvas
args.painter.drawImage(0, 0, img)