Ackland-Jones analysis¶
This modifier implements a method for identifying common crystalline and other structures based on an analysis of the distribution of angles formed by the pairs of neighbors of a central atom. The method is known as Ackland-Jones bond-angle method [Ackland and Jones, Phys. Rev. B 73, 054104]. The algorithm assigns a structural type to each particle having a local environment that matches one of the known structures (FCC, BCC, HCP, icosahedral).
Modifier outputs¶
The modifier outputs the classification results as a new particle property named Structure Type.
This information allows you to subsequently select particles of a certain structural type, e.g. using the
Select type modifier.
The structural type determined by the algorithm is encoded as an integer value:
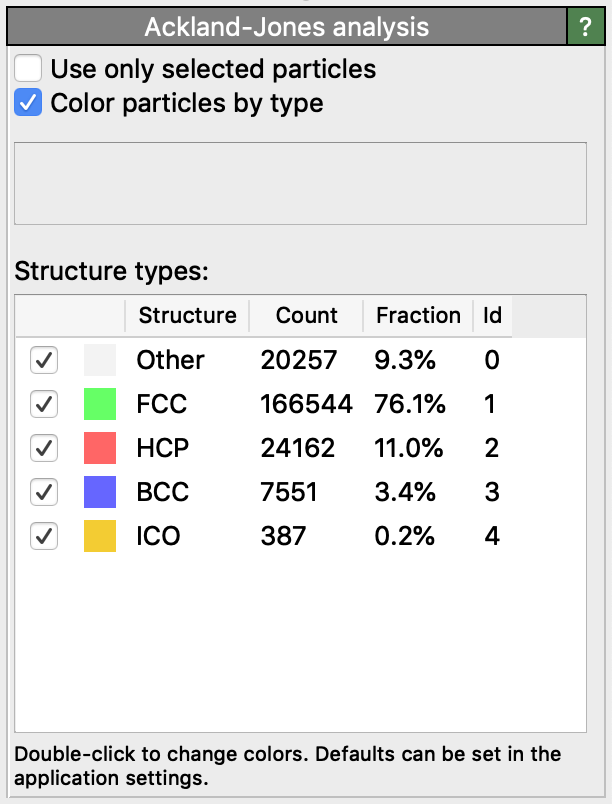
0 = Other, unknown coordination structure
1 = FCC, face-centered cubic
2 = HCP, hexagonal close-packed
3 = BCC, body-centered cubic
4 = ICO, icosahedral coordination
In addition, the modifier assigns colors to the particles (by setting the Color
particle property) to indicate their computed structural type. The color representing each structural type
can be customized by double-clicking the corresponding entry in the table or, permanently, in the
application settings dialog.
Furthermore, the modifier emits global attributes to the data pipeline reporting the total number of particles matching
each of the supported structural types. These attributes are named AcklandJones.counts.XXX, where XXX
stands for the name of a structure. These analysis statistics may be exported using OVITO’s data export function
or displayed as live information in the viewports using a text label.
Note
The modifier needs to see the complete set of input particles to perform the analysis. It should therefore be placed at the beginning of the data pipeline, preceding any modifiers that delete some of the particles.
The option Use only selected particles restricts the analysis to the currently selected particles. In this case, unselected particles will be ignored (as if they did not exist) and are all assigned the structure type “Other”. This option is useful if you want to identify defects in a crystal type not directly supported by the bond-angle analysis algorithm but having a sub-lattice that is supported.
Alternatives¶
OVITO provides implementations of other structure identification methods, for instance the Common neighbor analysis modifier, the Identify diamond structure modifier or the Polyhedral template matching modifier. Furthermore, the Centrosymmetry parameter modifier can be used to detect defects in crystal lattices.
See also
ovito.modifiers.AcklandJonesModifier (Python API)